Introduction
ST is a small tracing library written in C99. It is optimized for minimal data usage and aims to be easy to use while also being flexible enough to be integrated in hard real time systems.
Signal types supported are all integers up to 64 bit, integer arrays up to 32 bit, floats, doubles, events and strings.
How to use
ST requires the integrator to implement a few functions such as the timestamp and output functions in order to work. Apart from that, it is up to the specific use case how to stream data. In its simplest form, traces are processed with no real time demands on a dedicated interface. For more advanced usage, this library allows packets to be written, as the time budget allows, into any given buffer to send its contents via DMA to for instance a serial output. Due to its packet format, the output interface can still be utilitzed as is unless the text sent contains the packet preamble or epilouge, which are "\033[s" and "\033[u" respectively.
Simple example on Arduino
#include "st.h"
// Basic implementation of output and timestamp retrieval
void st_out(const char* const str, size_t len) { Serial.write(str, len); }
uint32_t st_timestamp(void) { return micros(); }
// No concurrency protection needed
void st_crit_on(uint32_t *h) {}
void st_crit_off(const uint32_t h) {}
static const size_t s_tracesize = 256;
static st_trace_t s_tracebuf[256];
void setup()
{
st_init(s_tracebuf, s_tracesize);
st_enable(st_drop); // drop traces on full buffer
st_u8trace("Serial.Ready", 0, false);
Serial.begin(2000000);
while (!Serial);
st_u8trace("Serial.Ready", 1, false);
}
void loop()
{
static unsigned sawtooth = 0;
if (sawtooth < 0xFFFF) sawtooth++;
else sawtooth = 0;
st_u32trace("Main.Sawtooth", sawtooth, false);
if (sawtooth == 4711) Serial.println("I can still be used with regular text.");
st_output(0, true, true); //send unlimited traces, compressed and clear console
st_diagtrace(); // add diagnostic traces
}
Basic operating principle
Traces are identified by a signal name, which may be hierarchical such as ExampleModule.Function.Value.
These must be statically accessible strings as they are later hashed when rendering traces.
Once a trace is rendered, the signal name is hashed using the BSD sum function.
This allows a client to identify a trace packet according to the source tree scanned.
For sending the traces to a client, they are put into a packet. A packet consist of a preamble, a flag byte, frame data and an epilouge. The preamble and epilouge are chosen to be the ANSI escape sequences for storing the current position, and restoring it.
The frame data may be compressed using fastlz, which is indicated by the Z flag in the packet. Regardless of compression, it is COBS encoded with delimiter 0033 to not interfere with the preamble or epilouge.
Frame data consists of multiple frames, COBS encoded with delimiter 0 and delimited with the same value. Each frame contains the signal hash, its type and depending on it a value ranging from 1-4 bytes and indexing information. Timestamps are sent in increments to conserve bandwidth. All trace functions feature a parameter which enables timestamp capture, if it is omitted this means no time delta is sent, making the trace appear to coincide with the last trace which captured a timestamp.
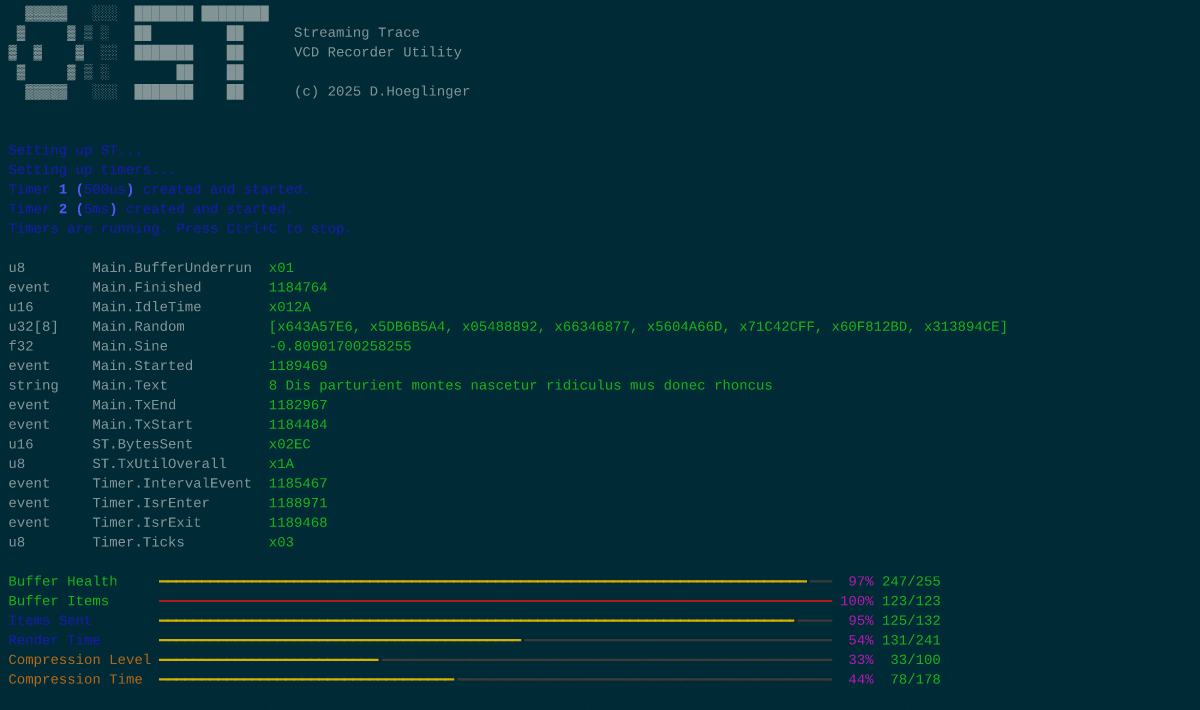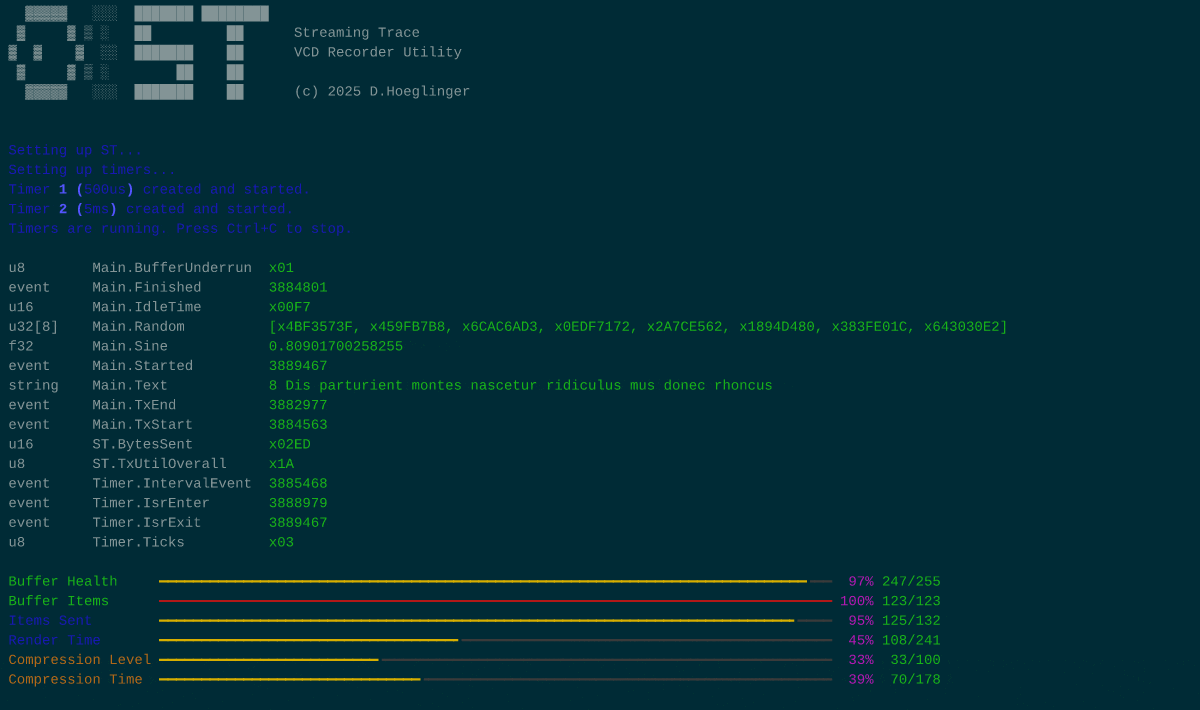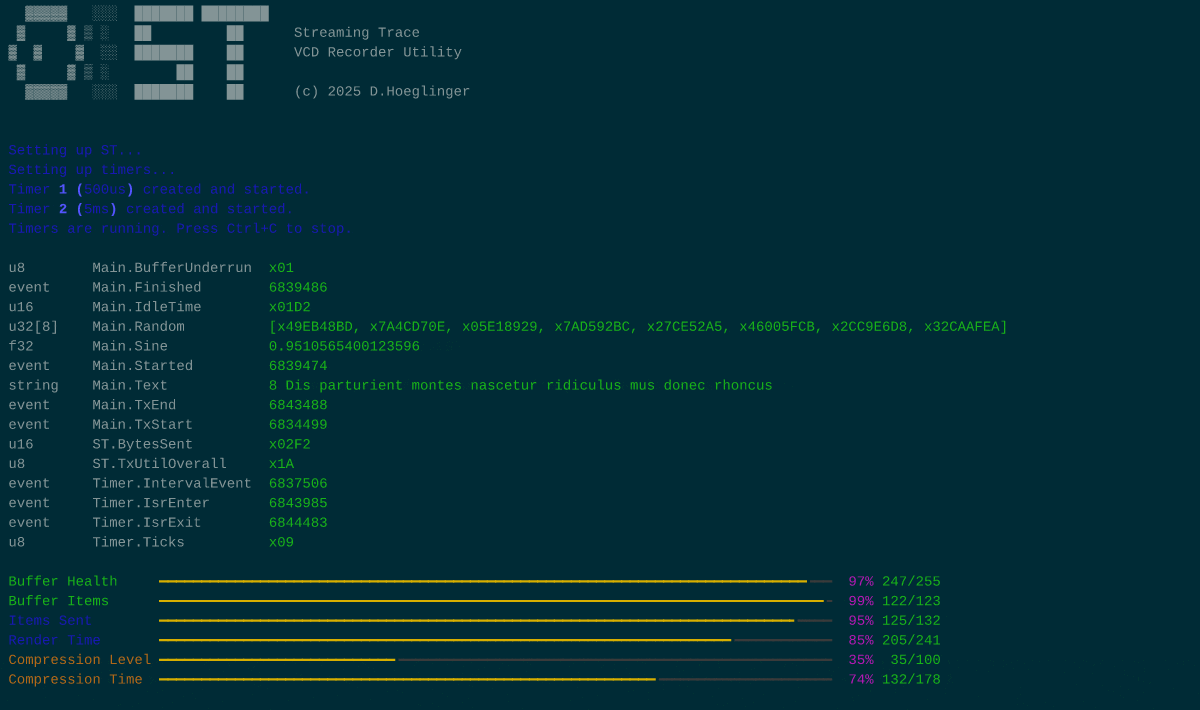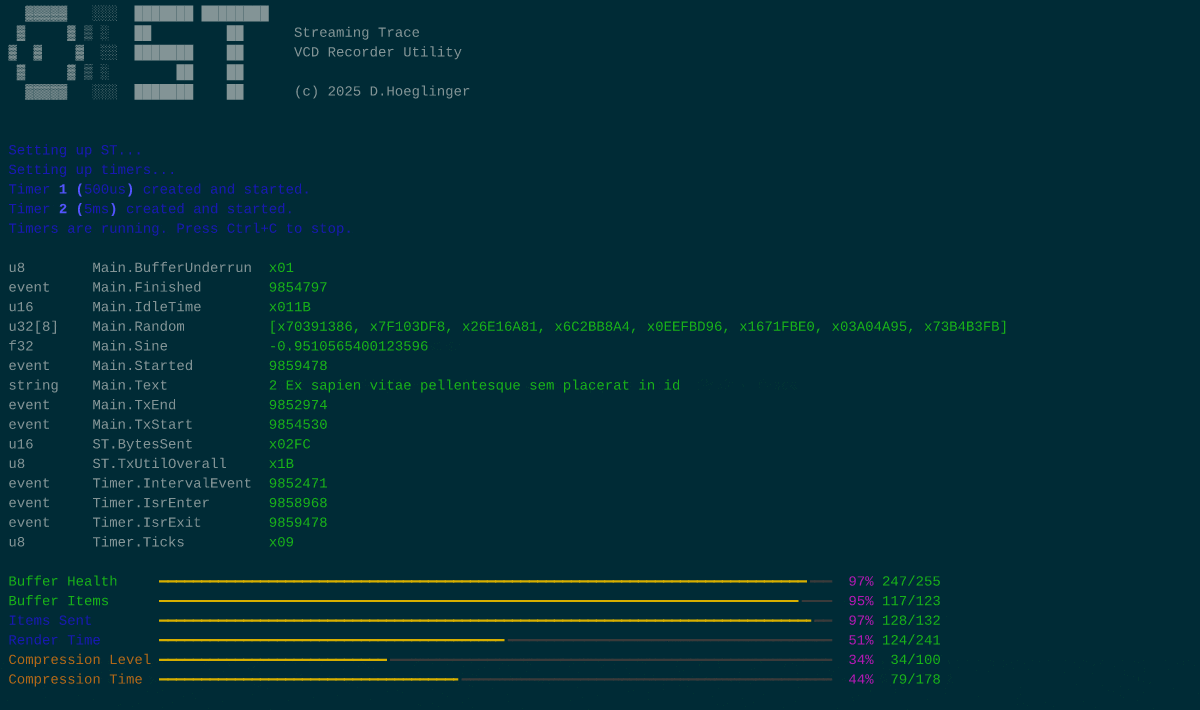
The recorder utility
The repository contains an example client application which captures packages and outputs the traces in a Value Change Dump. This script uses the PyVCD package which is the only dependency. Apart from that, this utility has every function integrated it'll need to decode a trace stream. It expects data via stdin, and displays any non-tracing traffic.
Example usage tracing remotely via SSH:
# Open /dev/ttyUSB0 via SSH and record to "trace.vcd"
# with timescale of 1 microsecond with diagnostics enabled
ssh user@host "picocom -b 921600 /dev/ttyUSB0" | \
./st_record.py -d trace.vcd -s ./Sources -t "1 us" --diagnostics
The resulting VCD can be inspected with dedicated programs such as GTKwave.
This script also features a TUI mode, displaying live diagnostic information. TUI mode requires the "rich" package in order to work.
Special Thanks
This repository uses code by the following people, so a thanks goes out to them!
- COBS algorithm with nonzero delimiter based on this Wren library by unknown
- FastLZ by ariya
- FastLZ Python native implementation by Oscar Diaz